bounce home test meniscal tears|Bounce Home Test : wholesaling Other tests for the knee menisci include: 1. Apley compression test 2. McMurrays Test 3. Ege's Test 4. Thessaly test See more I have fabricated parts in ovens under bags, and in autoclaves, including one so large that it has train rails for rolling the bond tools in and out. I've seen more than a couple .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Learn how F0 autoclaves quantify and optimize microbial inactivation by using the equivalent minutes of sterilization at 121.1°C. Discover the principles, formula, advantages, .
Evaluation of the Meniscus
With the patient supine, the therapist holds the patient’s heel of the foot with his hand and then passively flexes the knee. The knee is then passively allowed to extend. The knee should be able to fully extend “bounce home” with a sharp end feel. The test is positiveif full extension of the knee is not complete or has a . See moreThere are currently no studies investigating the sensitivity, specificity or diagnostic accuracy of the bounce home test as described originally. The bounce home test as described by Shybut and McGinty has sensitivity of 47%, a specificity of 67% . See moreOther tests for the knee menisci include: 1. Apley compression test 2. McMurrays Test 3. Ege's Test 4. Thessaly test See more
The Bounce Home Test is an orthopedic test to assess for intra-articular knee pathologies such as meniscus tears or loose bodies which can lead to excessive swelling, ultimately limited full knee extension.
The knee should be able to fully extend “bounce home” with a sharp end feel. The test is positive if full extension of the knee is not complete or has a rubbery end feel indicating a torn meniscus or other intra-articular pathology.
The Bounce Home Test is an orthopedic test to assess for intra-articular knee pathologies such as meniscus tears or loose bodies which can lead to excessive swelling, ultimately limited full knee extension.The Bounce home test evaluates for a possible limitation in the ability of the knee to fully extend. 24 A lack of full knee extension may signify a torn meniscus fragment, an other intra-articular pathology such as a loose body or joint effusion, or a displaced bucket handle tear that requires immediate orthopedic consultation. 24 The test is .Meniscal assessment: palpation & bounce home testDr. Mark Hutchinson's Knee, Shoulder and Hip/Groin Exam is a combined project of the University of Briti.
The bounce home test is used to detect meniscal pathology. To perform this test, have the patient lying supine and support the patient’s foot or ankle. Then, competely flex the knee and allow the knee to passively extend.
Bounce home test. With the patient lying supine, the surgeon grasps the foot, flexes completely the knee. The knee is then passively allowed to extend. The knee should extend completely or bounce home into extension with a sharp endpoint. A positive test occurs when full extension cannot be attained. Imaging Radiography Acute meniscal tears occur most often from twisting injuries; chronic degenerative tears occur in older patients and can occur with minimal twisting or stress. Left untreated, large complex tears can impair smooth motion of the knee, cause joint effusions, and may lead to premature osteoarthritis.
The bounce home test assesses passive knee range of motion to aid in the diagnosis of meniscus tears. This test begins with the patient positioned supine with full knee flexion. The examiner cups the foot of the affected extremity and allows the knee to passively fall into full extension.The bounce home test assesses passive knee range of motion to aid in the diagnosis of meniscus tears. This test begins with the patient positioned supine with full knee fl exion. The examiner cups the foot of the affected extremity and allows the knee to passively fall into full extension.The Bounce Home Test evaluates for meniscal tears by assessing the ability to fully extend the knee after flexion. The McMurray Test involves manipulating the knee joint by rotating and extending it to detect meniscal tears based on the presence of pain, clicking, or locking.The knee should be able to fully extend “bounce home” with a sharp end feel. The test is positive if full extension of the knee is not complete or has a rubbery end feel indicating a torn meniscus or other intra-articular pathology.
The Bounce Home Test is an orthopedic test to assess for intra-articular knee pathologies such as meniscus tears or loose bodies which can lead to excessive swelling, ultimately limited full knee extension.The Bounce home test evaluates for a possible limitation in the ability of the knee to fully extend. 24 A lack of full knee extension may signify a torn meniscus fragment, an other intra-articular pathology such as a loose body or joint effusion, or a displaced bucket handle tear that requires immediate orthopedic consultation. 24 The test is .
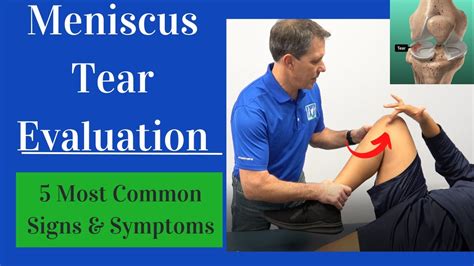
Bounce Home Test
Meniscal assessment: palpation & bounce home testDr. Mark Hutchinson's Knee, Shoulder and Hip/Groin Exam is a combined project of the University of Briti.The bounce home test is used to detect meniscal pathology. To perform this test, have the patient lying supine and support the patient’s foot or ankle. Then, competely flex the knee and allow the knee to passively extend.Bounce home test. With the patient lying supine, the surgeon grasps the foot, flexes completely the knee. The knee is then passively allowed to extend. The knee should extend completely or bounce home into extension with a sharp endpoint. A positive test occurs when full extension cannot be attained. Imaging Radiography Acute meniscal tears occur most often from twisting injuries; chronic degenerative tears occur in older patients and can occur with minimal twisting or stress. Left untreated, large complex tears can impair smooth motion of the knee, cause joint effusions, and may lead to premature osteoarthritis.
The bounce home test assesses passive knee range of motion to aid in the diagnosis of meniscus tears. This test begins with the patient positioned supine with full knee flexion. The examiner cups the foot of the affected extremity and allows the knee to passively fall into full extension.
The bounce home test assesses passive knee range of motion to aid in the diagnosis of meniscus tears. This test begins with the patient positioned supine with full knee fl exion. The examiner cups the foot of the affected extremity and allows the knee to passively fall into full extension.

These diagnostic tests are intended to complement one another and play an important role, along with biological and chemical indicators, in ensuring an effective steam sterilization process. All these tools are .
bounce home test meniscal tears|Bounce Home Test